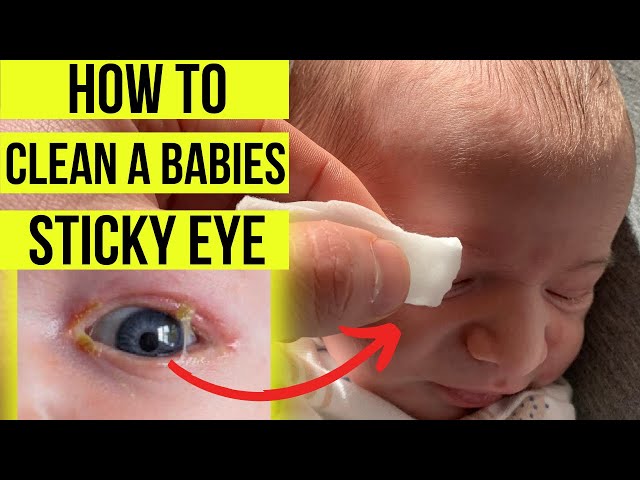
When a toddler has a green discharge coming from their eye, it is typically a sign of a bacterial infection. The discharge may be thick and sticky, and it may also be accompanied by redness, swelling, and pain. In some cases, the infection may also cause the toddler to have difficulty opening their eye.
It is important to take your toddler to the doctor if they have a green discharge coming from their eye. The doctor will be able to diagnose the infection and prescribe the appropriate treatment. Treatment for a bacterial eye infection typically involves antibiotic eye drops or ointment.
In most cases, a bacterial eye infection will clear up within a few days of treatment. However, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions carefully to ensure that the infection does not come back.
Green Discharge from Eye Toddler
When a toddler has a green discharge coming from their eye, it is typically a sign of a bacterial infection. The discharge may be thick and sticky, and it may also be accompanied by redness, swelling, and pain. In some cases, the infection may also cause the toddler to have difficulty opening their eye.
- Cause: Bacterial infection
- Symptoms: Green discharge, redness, swelling, pain, difficulty opening the eye
- Treatment: Antibiotic eye drops or ointment
- Prevention: Good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the eyes
- Complications: If left untreated, a bacterial eye infection can lead to more serious complications, such as conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, and even blindness.
- Outlook: With prompt treatment, most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days.
It is important to take your toddler to the doctor if they have a green discharge coming from their eye. The doctor will be able to diagnose the infection and prescribe the appropriate treatment. Treatment for a bacterial eye infection typically involves antibiotic eye drops or ointment. In most cases, a bacterial eye infection will clear up within a few days of treatment. However, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions carefully to ensure that the infection does not come back.
Cause
A bacterial infection is the most common cause of a green discharge from the eye in toddlers. Bacteria can enter the eye through a variety of means, such as contact with contaminated objects or surfaces, or through the spread of bacteria from another part of the body, such as the nose or throat. Once bacteria enter the eye, they can quickly multiply and cause an infection. Bacterial eye infections are typically characterized by a green or yellow discharge, as well as redness, swelling, and pain.
It is important to seek medical attention promptly if your toddler has a green discharge from their eye, as bacterial eye infections can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Treatment for a bacterial eye infection typically involves antibiotic eye drops or ointment. With prompt treatment, most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days.
Preventing bacterial eye infections in toddlers is important. Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the eyes, can help to reduce the risk of infection. If your toddler has a weakened immune system, they may be more susceptible to bacterial eye infections. In these cases, it is important to take extra precautions to prevent infection, such as avoiding contact with sick people and staying away from crowded places.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a green discharge from the eye in toddlers, which include green discharge, redness, swelling, pain, and difficulty opening the eye, are all indicative of an underlying bacterial infection. These symptoms are important to recognize because they can help to differentiate a bacterial eye infection from other, less serious conditions, such as viral conjunctivitis. Bacterial eye infections require prompt treatment with antibiotics to prevent serious complications, such as conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, and even blindness.
The green discharge from the eye is caused by the presence of bacteria in the eye. The bacteria produce a toxin that irritates the conjunctiva, the clear membrane that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelid. This irritation leads to the redness, swelling, and pain. The pain can be severe enough to make it difficult for the toddler to open their eye.
It is important to take your toddler to the doctor if they have any of the symptoms of a bacterial eye infection. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Treatment
When a toddler has a green discharge coming from their eye, it is typically a sign of a bacterial infection. The bacteria can cause the conjunctiva, the clear membrane that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelid, to become inflamed and irritated. This inflammation can lead to redness, swelling, pain, and a green discharge.
Antibiotic eye drops or ointment are the most effective treatment for a bacterial eye infection in toddlers. The antibiotic will kill the bacteria and allow the infection to heal. Treatment typically lasts for 7-10 days.
-
Benefits of antibiotic eye drops or ointment
Antibiotic eye drops or ointment are effective in treating bacterial eye infections in toddlers. They are also relatively easy to administer and have few side effects. -
Importance of completing the full course of treatment
It is important to complete the full course of treatment, even if the symptoms improve. This will help to ensure that the infection is completely cleared and prevent it from coming back. -
Potential side effects of antibiotic eye drops or ointment
Antibiotic eye drops or ointment can cause some side effects, such as redness, itching, and burning. These side effects are usually mild and go away after a few days. -
Alternatives to antibiotic eye drops or ointment
In some cases, a bacterial eye infection in toddlers may be treated with oral antibiotics. However, antibiotic eye drops or ointment are typically the preferred treatment.
If your toddler has a green discharge coming from their eye, it is important to take them to the doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment. Antibiotic eye drops or ointment are the most effective treatment for a bacterial eye infection in toddlers.
Prevention
Practicing good hygiene is essential for preventing the spread of bacteria and viruses, which can cause a variety of infections, including bacterial eye infections in toddlers. Bacteria and viruses can be spread through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces, or through the spread of bacteria or viruses from another part of the body, such as the nose or throat. Touching the eyes with unwashed hands is a common way for bacteria or viruses to enter the eye and cause an infection.
-
Washing hands frequently
Washing hands frequently with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses. This is especially important for toddlers, who are more likely to put their hands in their mouths and touch their eyes. Toddlers should be taught to wash their hands frequently, especially after using the bathroom, before eating, and after playing outside.
-
Avoiding touching the eyes
Another important way to prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses to the eyes is to avoid touching the eyes with unwashed hands. This can be difficult for toddlers, who are often curious and may not realize that they are touching their eyes. Parents and caregivers should supervise toddlers to prevent them from touching their eyes, and should remind them to wash their hands frequently.
By practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the eyes, parents and caregivers can help to reduce the risk of their toddlers developing a bacterial eye infection.
Complications
A bacterial eye infection is a common condition in toddlers, but it is important to seek treatment promptly to prevent serious complications. If left untreated, a bacterial eye infection can lead to conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, and even blindness. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the clear membrane that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelid. Corneal ulcer is a sore on the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye. Blindness is a loss of vision that cannot be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
The green discharge from the eye is a sign of a bacterial infection. The bacteria produce a toxin that irritates the conjunctiva, causing it to become inflamed and swollen. This inflammation can lead to redness, pain, and a green discharge. If the infection is not treated, the bacteria can spread to the cornea and cause a corneal ulcer. A corneal ulcer is a serious condition that can lead to blindness if it is not treated promptly.
It is important to take your toddler to the doctor if they have a green discharge from their eye. The doctor will be able to diagnose the infection and prescribe the appropriate treatment. Treatment for a bacterial eye infection typically involves antibiotic eye drops or ointment. With prompt treatment, most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days.
Preventing bacterial eye infections in toddlers is important. Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the eyes, can help to reduce the risk of infection.
Outlook
The outlook for toddlers with a green discharge from the eye is generally good with prompt treatment. Bacterial eye infections are common in toddlers, but they can be effectively treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointment. Most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days of treatment.
-
Importance of early diagnosis and treatment
It is important to take your toddler to the doctor if they have a green discharge from their eye. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications, such as conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, and even blindness.
-
Effectiveness of antibiotic treatment
Antibiotic eye drops or ointment are effective in treating bacterial eye infections in toddlers. The antibiotic will kill the bacteria and allow the infection to heal.
-
Duration of treatment
Treatment for a bacterial eye infection in toddlers typically lasts for 7-10 days. It is important to complete the full course of treatment, even if the symptoms improve. This will help to ensure that the infection is completely cleared and prevent it from coming back.
-
Prevention of complications
Prompt treatment of a bacterial eye infection can help to prevent serious complications, such as conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, and blindness.
By understanding the outlook for bacterial eye infections in toddlers and the importance of prompt treatment, parents and caregivers can help to ensure that their toddlers receive the best possible care.
FAQs
This section addresses common concerns and misconceptions regarding green discharge from the eye in toddlers.
Question 1: What causes a green discharge from the eye in toddlers?
Answer: A green discharge from the eye in toddlers is typically caused by a bacterial infection. The bacteria can enter the eye through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces, or through the spread of bacteria from another part of the body, such as the nose or throat.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of a bacterial eye infection in toddlers?
Answer: The symptoms of a bacterial eye infection in toddlers include green or yellow discharge from the eye, redness, swelling, pain, and difficulty opening the eye.
Question 3: How is a bacterial eye infection in toddlers treated?
Answer: A bacterial eye infection in toddlers is typically treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointment. The antibiotic will kill the bacteria and allow the infection to heal.
Question 4: How long does it take for a bacterial eye infection in toddlers to clear up?
Answer: With prompt treatment, most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days.
Question 5: How can I prevent my toddler from getting a bacterial eye infection?
Answer: You can help prevent your toddler from getting a bacterial eye infection by practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the eyes.
Question 6: What are the potential complications of a bacterial eye infection in toddlers?
Answer: If left untreated, a bacterial eye infection in toddlers can lead to serious complications, such as conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, and even blindness.
Summary: Green discharge from the eye in toddlers is typically caused by a bacterial infection. The symptoms of a bacterial eye infection in toddlers include green or yellow discharge from the eye, redness, swelling, pain, and difficulty opening the eye. Bacterial eye infections in toddlers are treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointment. With prompt treatment, most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days.
Transition to the next article section: It is important to take your toddler to the doctor if they have a green discharge from their eye. The doctor will be able to diagnose the infection and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Tips for Managing Green Discharge from Eye in Toddlers
If your toddler has a green discharge coming from their eye, it is important to take them to the doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment. Bacterial eye infections are common in toddlers, but they can be effectively treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointment. Most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days of treatment.
Tip 1: Wash your toddler’s hands frequently with soap and water. This will help to prevent the spread of bacteria to the eyes.
Tip 2: Avoid touching your toddler’s eyes. If you need to touch their eyes, wash your hands first.
Tip 3: Keep your toddler’s eyes clean. Use a clean washcloth or cotton ball to wipe away any discharge from the eyes.
Tip 4: Do not share towels or washcloths with your toddler. This can help to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Tip 5: If your toddler is taking antibiotics for a bacterial eye infection, be sure to give them the full course of medication. This will help to ensure that the infection is completely cleared.
Tip 6: If your toddler’s symptoms do not improve after a few days of treatment, or if they get worse, take them back to the doctor.
Tip 7: If your toddler has a weakened immune system, they may be more susceptible to bacterial eye infections. Talk to your doctor about ways to boost your toddler’s immune system.
Tip 8: Good hygiene is the best way to prevent bacterial eye infections. Make sure your toddler washes their hands frequently and avoids touching their eyes.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
- Green discharge from the eye in toddlers is typically caused by a bacterial infection.
- Bacterial eye infections in toddlers are treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointment.
- With prompt treatment, most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days.
- Good hygiene is the best way to prevent bacterial eye infections.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
By following these tips, you can help to prevent and treat bacterial eye infections in your toddler.
Conclusion
A green discharge from the eye in toddlers is typically a sign of a bacterial infection. Bacterial eye infections are common in toddlers, but they can be effectively treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointment. Most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days of treatment.
It is important to take your toddler to the doctor if they have a green discharge from their eye. The doctor will be able to diagnose the infection and prescribe the appropriate treatment. Treatment for a bacterial eye infection typically involves antibiotic eye drops or ointment. With prompt treatment, most bacterial eye infections in toddlers will clear up within a few days.
Preventing bacterial eye infections in toddlers is important. Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the eyes, can help to reduce the risk of infection.
Youtube Video: